HKDC1 protein found crucial to maintaining two mitochondria subcellular structures, mitochondria and lysosomes
Originally published by Osaka University, on January 1, 2024
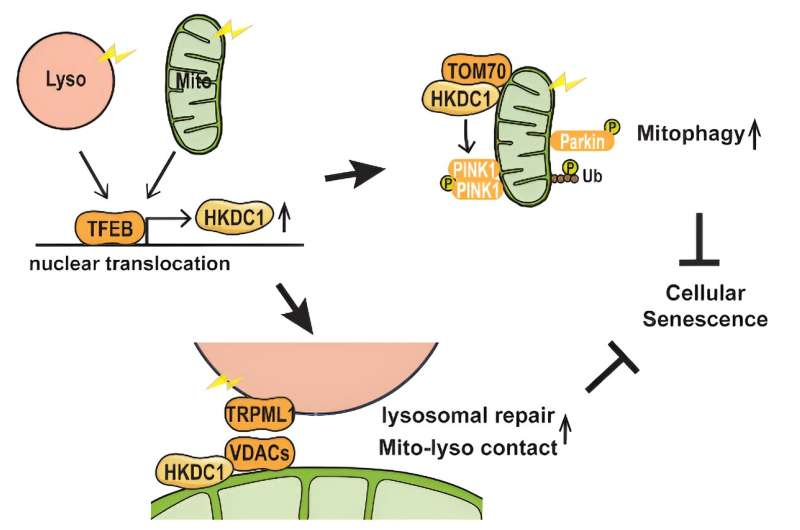
Overview: Both mitochondrial and lysosomal stress stimulate TFEB nuclear translocation, followed by increased HKDC1 expression. HKDC1 stabilizes PINK1 through interaction with TOM70, thereby facilitating PINK1/Parkin-dependent mitophagy. Additionally, HKDC1 and the VDAC proteins with which it interacts are important for repair of damaged lysosomes and maintaining mitochondria–lysosome contact. HKDC1 prevents DNA damage–induced cellular senescence by maintaining mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis. Credit: 2024 Cui et al., HKDC1, a target of TFEB, is essential to maintain both mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, preventing cellular senescence, PNAS.
Just as healthy organs are vital to our well-being, healthy organelles are vital to the proper functioning of the cell. These subcellular structures carry out specific jobs within the cell; for example, mitochondria power the cell, and lysosomes keep the cell tidy.
Although damage to these two organelles has been linked to aging, cellular senescence, and many diseases, the regulation and maintenance of these organelles have remained poorly understood. Now, researchers at Osaka University have identified a protein, HKDC1, that plays a key role in maintaining these two organelles, thereby acting to prevent cellular aging.


Comments
Post a Comment